What is in this article?
If you are interested in history, you probably know about the effects of the Industrial Revolution on the course of history and human civilization.
This era started in Great Britain in 1760 and continued to spread through Continental Europe to the United States of America until mid-1800s, when manual labor was replaced by machine-manufacturing, and the use of water and steam power played a key role. At this very point, we can talk about James Watt, one of the people who made the Industrial Revolution happen.
Known as the inventor of the first steam machine, which is a common misconception, James Watt was actually not the person who invented it but who turned an existing solution into an efficient and commonly used method.
Let’s take a closer look at the life and work of James Watt, who took the first step towards the Industrial Revolution with the steam engines he developed.
Life of James Watt
James Watt was born on January 19, 1736 in Greenock, Scotland, to a shipbuilding father and a mother from a wealthy family.
As a susceptible kid, James Watt struggled with diseases throughout his childhood. Due to such susceptibility, the first part of his education was provided by his mother at home, while he acquired a craft from his father, who was engaged in carpentry and shipbuilding. James Watt improved himself greatly in his father’s shipbuilding work, specializing in the manufacture of numerous tools used in ships.
 After his mother passed away and his father fell down on the job, a new era started in the life of James Watt, who started to have an interest in the manufacture of mathematical instruments when he was 17-18. For this purpose, he went to London in 1755, and despite his health problems made it difficult, he managed to get the required training and learned the ropes from dab hands.
After his mother passed away and his father fell down on the job, a new era started in the life of James Watt, who started to have an interest in the manufacture of mathematical instruments when he was 17-18. For this purpose, he went to London in 1755, and despite his health problems made it difficult, he managed to get the required training and learned the ropes from dab hands.
He returned home in 1757 and started his own business in the manufacture and repair of mathematical instruments at the Glasgow University. Responsible for repairing the instruments at the university, James Watt got the chance to become friends with scientists there.
In 1763, the university asked for Watt’s help to repair the Newcomen steam engine they developed. Shifting his focus to steam engines, James Watt found a way to improve these machines. With his studies underway, he met John Roebuck, an English physician, chemist and inventor, and got funding to accomplish his projects. Although Roebuck owned two-thirds of this partnership, James Watt considered this an opportunity to materialize his steam engine but it took him 11 years to do so.
Another turning point in James Watt’s life was when his partner Roebuck went bankrupt in 1772. Roebuck transferred his patent rights to Matthew Boulton, an English businessman and engineer.
Boulton, as an inventor and a visionary man, addressed the deficiencies for James Watt to materialize his invention. These two men had a friendship that lasted for long years and got a fame that would be remembered by the generations to come, as well as a wealth that allows for a comfortable period of retirement.
James Watt became financially strong with help from Boulton and built two functional steam engines in 1776. The steam engine was preferred in mining in the subsequent years due to its efficiency, to which Boulton added circular motion instead of reciprocating motion thanks to his business mindset. This allowed Watt’s steam engines to be used in corn, malt and cotton plants in addition to mines.
Watt didn’t settle for this and in the following years, he added a centrifugal governor to the steam engine to automatically control the engine speed. In 1790, he invented the pressure gauge, again to be used in these engines.
In 1800, Watt and Boulton handed over their work to their children and retired.
What Did James Watt Invent?
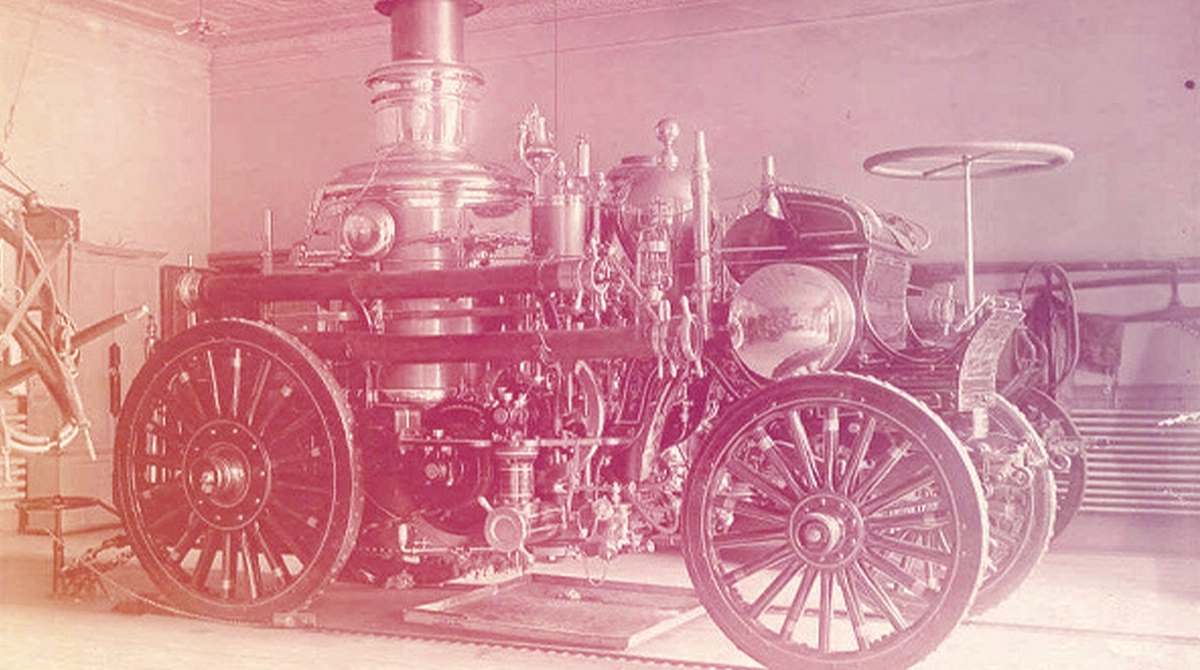 The moderns steam engine developed by James Watt is his most important invention. One of the keystones of the Industrial Revolution, Watt steam engines are much more valuable than thought for the human progress.
The moderns steam engine developed by James Watt is his most important invention. One of the keystones of the Industrial Revolution, Watt steam engines are much more valuable than thought for the human progress.
In addition to inventions like sun and planetary gears which continuously improved the steam engine and made it more capable, he continued his work even after retirement and made numerous inventions like the copying press, distance measuring with telescope, improved oil lamps, the sculpture copying machine and the steam roller.
The Smethwick Engine manufactured in 1779, the oldest functional steam engine in the world, is exhibited at the Birmingham Science Museum. Designed by Boulton and Watt, this engine was used to replace water equivalent to 1,500 buckets per minute.
The horsepower or hp, which is especially used to state the power of an engine, was also used for the first time by James Watt. Horsepower defines the work done by a force of 550 pounds acting through a horse’s one foot in one second. It equals to a force of 33,000 pounds per minute. A force of 1 hp corresponds to 746 watts approximately.
How Does the Modern Steam Engine Work?
We can say that the studies on air mechanics by the mathematician Heron in 75 A.C. is the basis for the steam technology, which is the starting point of the Industrial Revolution.
Humanity, on the other hand, met the steam machines with the steam pump developed in 1698 by Thomas Savery to drain water from mines. Savery’s machine was based on the principle that the vacuum effect created with steam power moved the water through pipes. In 1712, Thomas Newcomen combined the vacuum and piston technologies to invent an atmospheric engine. With a power the drain water from a depth of 300 feet, this machine was considered a very important invention back then.
 James Watt met the Newcomen engine when he was asked to repair it while working at the Glasgow University in 1763. Noticing that the engine can work more efficiently with a separate cooling chamber, James Watt put the modern steam machines he developed in practice.
James Watt met the Newcomen engine when he was asked to repair it while working at the Glasgow University in 1763. Noticing that the engine can work more efficiently with a separate cooling chamber, James Watt put the modern steam machines he developed in practice.
Unlike Newcomen’s engine, the Watt steam machine has a separate condensation chamber called a condenser. This means separate sections for the operating cylinder and condensation. The steam is transferred from the boiler to the cylinder where the piston is located, ensuring up and down movement of the piston. When the piston reaches the highest position in the cylinder, steam inlet is closed and the bypass valve to the condenser is opened. This ensures that the high pressure steam goes from the piston cylinder to the condensation section. When the piston is going downwards, the steam is converted into water in the condensation container by cooling down mostly using the cold water obtained from wells as well as mines. Conserving a large portion of its temperature, this water is used for re-generating steam. This solution by James Watt eliminated the need to repeatedly heat and cool down the piston, as is the case with Newcomen’s machine. Watt’s machine reduced fuel consumption by one-thirds compared to Newcomen’s machines.
In the following years, James Watt made some advancements such as adding the capability of making circular movements to its machine using the sun-planetary gear system he invented. In addition to its intended use, which was draining water from mines, it was also used for production in factories.
The modern steam machine by James Watt is one of the keystones of the Industrial Revolution, both because it allowed for a more efficient extraction of mines and because it changed the method of manufacturing.
James Watt’s Works and Awards
Although he did not get grand awards for his inventions when alive, he later became a well-known and respected person thanks to the steam engines he made. One of the members of the Lunar Society comprising of reputable writers and scientists in Birmingham, James Watt was chosen a member of the London Royal Society in 1785. He also got proposals from numerous science groups admiring his work.
The financial problems he experienced during his youth ended at a relatively young age and he had a comfortable retirement period, which can also be considered a reward for James Watt’s work.
The international standard power unit “Watt” was named after James Watt. Used as a power unit, Watt (W) represents the energy flow in a circuit and is found by multiplying the current flowing through the circuit by the voltage passing through the circuit.
The formula for Watt calculation is:
Power (Watt) = Voltage (Volt) x Current (I, amperes)
Although he was not rewarded medals in his lifetime, it was decided to give the James Watt International Gold Metal Award every two years as an engineering prize by the United Kingdom Institute of Mechanical Engineers, starting from 1937, for the two-hundredth anniversary of his birth.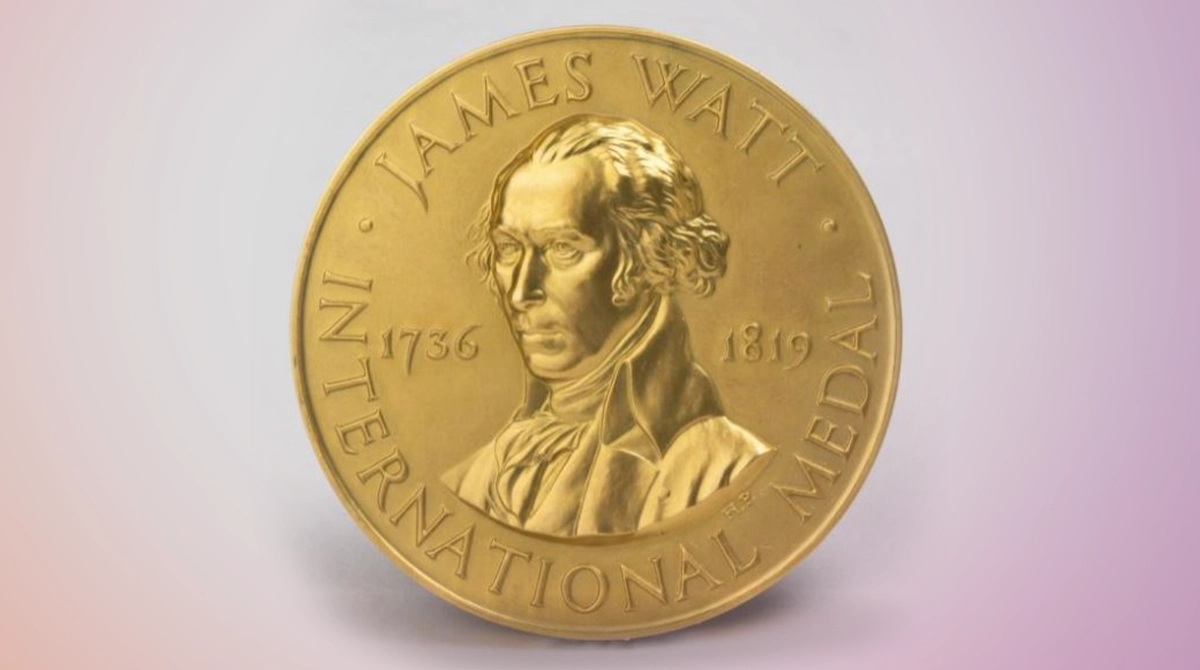
Don’t you think it is really impressive that an invention made in the mid-1700s started a transformation and development era like the Industrial Revolution, which changed the future of all humanity? Share your thoughts with us on the fact that James Watt’s steam engine is the basis for the modern manufacturing system in today’s world.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership






Leave a Comment