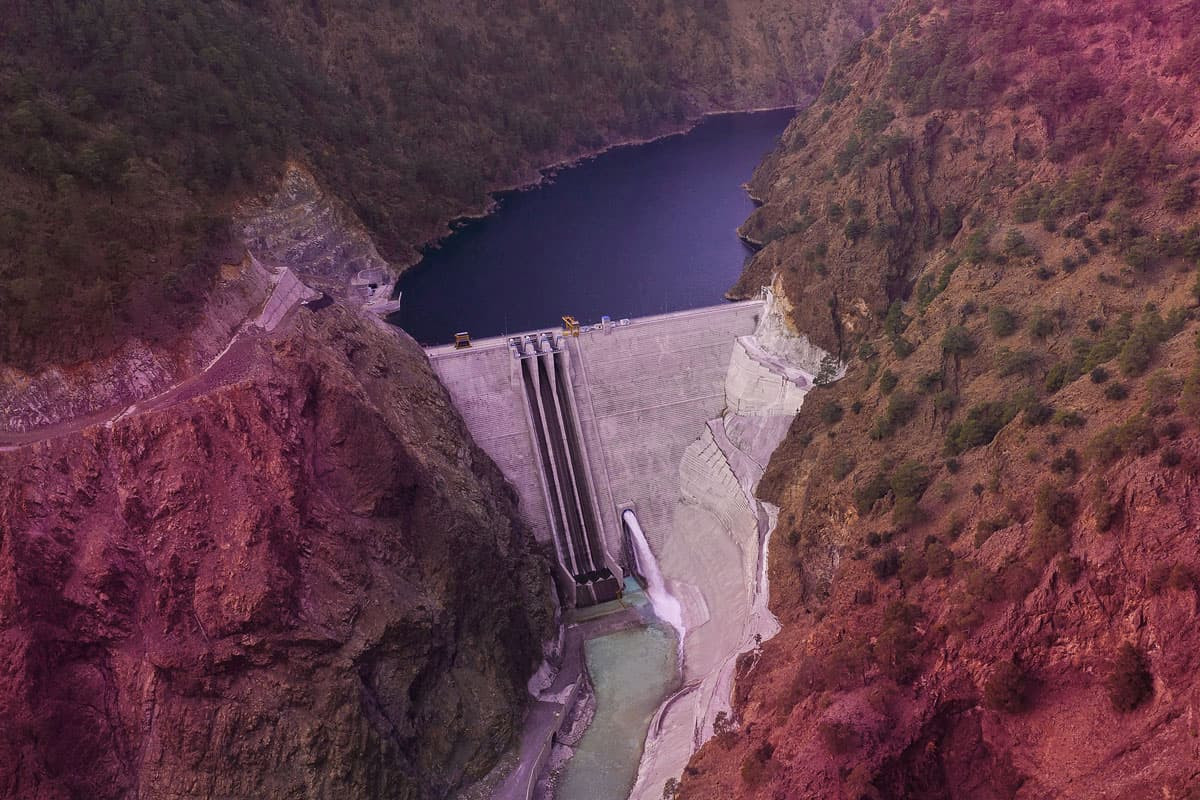

What is Hydroelectric Energy and How is It Produced?
What is in this article?
The daily decrease of non-renewable energy sources forces mankind to search for renewable and sustainable resources. The gradual growth of the world population leads to an increase in energy demand.
Therefore, renewable and environmentally friendly energy sources are gaining importance. Hydroelectric energy, which is one of the renewable resources, is derived from the power of flowing water such as streams, rivers and waterfalls.
Hydroelectric power, derived from the Greek word hydro meaning water, has been used for many years. In both ancient Greece and ancient Rome, people used flowing water to grind grain and make flour and bread. Turbines were built with impellers that turned with the flowing water, and these turbines were used for a long time.
Another source of hydroelectric power is water mills. Widely used until the 1900s, water mills were in the form of large wheels on riverbanks.
In addition to grinding grain, water mills also provided energy for activities such as cutting wood or making steel.
Continue reading our article to learn more about hydraulic power and power plants, parts and types of power plants, and the use of hydraulic power.
What is Hydraulic Power?
In its simplest definition, hydraulic power is energy derived from water. Hydraulic power has been the most widely used sources of energy since the dawn of mankind. In hydraulic power generation, the potential energy of water is converted into kinetic energy and electricity is generated. Electricity is generated by the force of water transferred from the upper levels to the lower levels.
What is Hydroelectric Power Plant (HPP)?
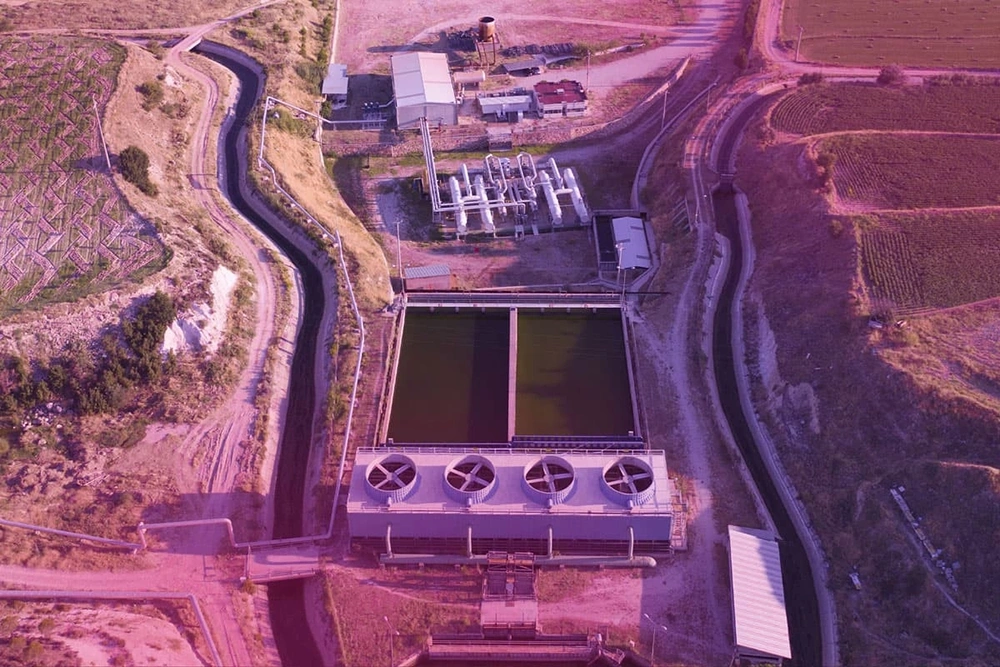
Hydroelectric energy is one of the most widely used renewable energy sources. In order to use this energy, dams are built and water is dammed up. Thanks to the kinetic energy of this dammed water, electric energy is generated in the turbine. Hydroelectric power plants are also built for this purpose.
 The hydroelectric potential of a country is determined on the basis of calculating the use of all natural water flows within the country's borders with an efficiency of 100%.
The hydroelectric potential of a country is determined on the basis of calculating the use of all natural water flows within the country's borders with an efficiency of 100%.
This is the theoretical gross hydropower potential of a country. However, it is not possible to fully utilize this potential.
Hydroelectric energy represents a large potential resource, especially for developing countries. Among the available energy sources, it is one of the cleanest.
In meeting the world's energy needs, the environment should also be taken into account. Therefore, turning to renewable resources is gaining importance day by day.
At this point, hydraulic energy, which draws its energy from the water cycle, increases efficiency and responds well to energy needs, can be preferred.
The reason why hydroelectric energy is renewable is the natural cycle of water. Water evaporates, clouds form, then it rains and the water returns to the earth. Because of this cycle, using water as an energy source is a safe and ideal choice.
Worldwide, 71% of the electricity generated from renewable energy sources is hydroelectric.
Thanks to hydraulic energy, which is generated depending on the precipitation regime, large amounts of electricity can be provided, which is needed, for example, to run factories and light cities.
In hydroelectric power plants, electricity is generated by harnessing the power of flowing water. The amount of energy generated varies depending on the flow or fall velocity of the water. Strongly flowing water contains a large amount of energy. This energy is converted into electrical energy and used.
What are the Main Components of Hydroelectric Power Plants? How is Energy Generated from Hydropower?
The main components of HEPPs can be listed as follows:
- Generators
- Hydraulic turbines
- Tunnels
- Transformers
- Penstock
- Water intake reservoir
- Backwater behind the dam
- The parts where the water flows through the turbine and exits again
- Devices for controlling the distribution of electrical energy through water flow
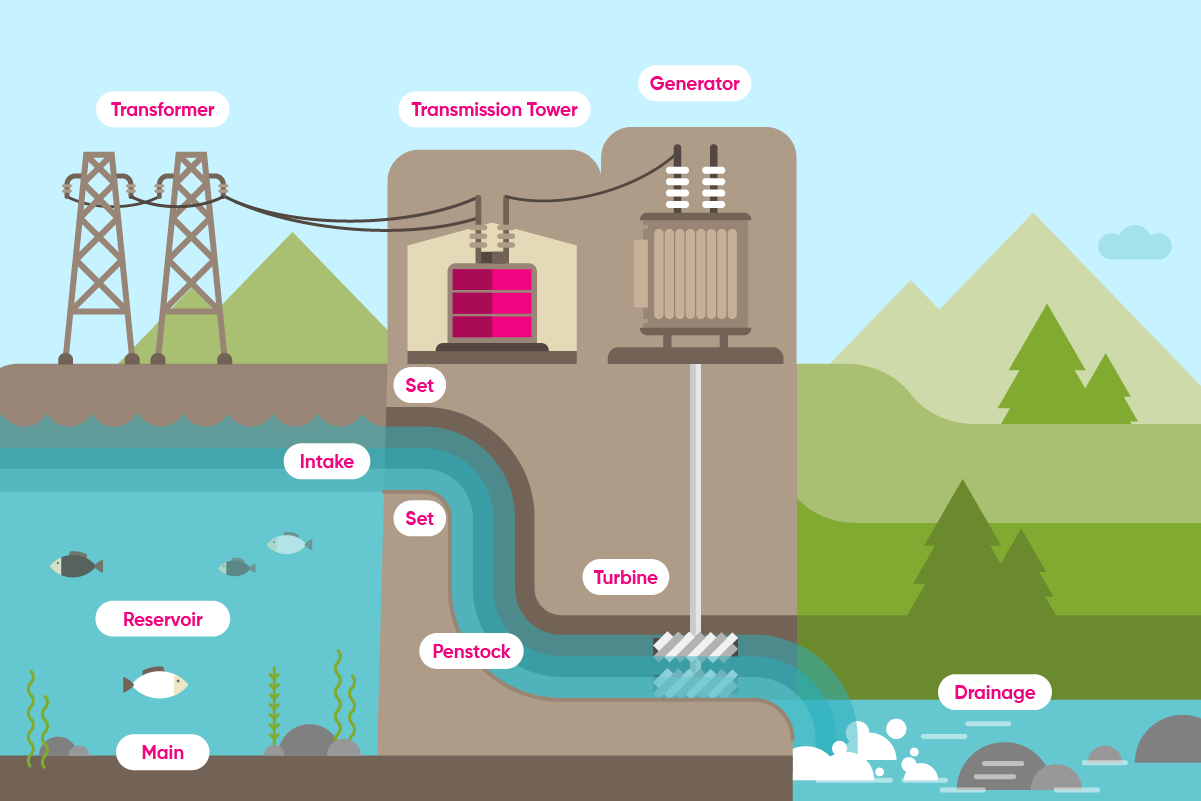
In these systems, the kinetic and potential energy of the water represents the input power.
Penstocks are large pipes or tunnels that carry water to turbines.
Turbines convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy.
Transformers amplify the alternating voltage produced by generators to transmit it over long distances.
The turbines rotate thanks to the potential energy of the water flowing from the reservoir to the penstock and the kinetic energy it gains until it reaches the turbine. This is how electrical energy is generated.
Where is the Energy of Hydropower Used?
Hydraulic energy has been used in various fields, such as cutting trees and grain production. The main purpose of installing hydroelectric power plants is to generate electricity. It has a high preference rate due to its low cost compared to other energy sources and its environmental friendliness.
Hydropower is also used to close the energy deficit. Fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas are decreasing day by day depending on consumption. As a result, the demand for natural, renewable and sustainable resources is increasing. In addition to the sun and wind, the power of water is also being harnessed to meet this demand.
What are the Types of Hydroelectric Power Plants?
Hydroelectric power plant types can be classified in several ways. These classifications take into account the characteristics of the water body in which the power plant is built, the head, the material of the dam, the capacity of the power plant, the place of construction, and the type and value of the energy obtained.
Depending on the characteristics of the water in which they are installed, HEPPs are classified into five types. These are river, reservoir, tidal, pumping and depression.
-
River Type (No dam) HEPP
This type of HEPP does not require the construction of a dam to generate electricity. Electric power is generated by harnessing the natural flow of water. The flow is first directed into a canal or tunnel and the water is tilted.
The turbine is installed at the upper part of the canal like a bridge. It should be noted that the annual flow of the river where the power plant is installed should be sufficient for minimum power generation. Also, the river must have the potential to turn the turbine shaft.
-
Reservoir Type (Dam) HEPP
The reservoir type, i.e. HEPP with dam, is the best known and most commonly used method in the world. With this type of HEPP, a dam is first built and water is accumulated.
This accumulated water has a certain potential energy. In this way, electricity can be generated even in dry years. Electric energy is generated with this water flowing through the turbines in the dams.

-
HEPP Pumped Storage Plant
The HEPP pumped storage plant is not used to generate electrical energy, but to store surplus energy.
With this method, water is pumped into an elevated reservoir during the hours when electricity demand and price are low and electricity is abundant.
During the hours when demand is high and electric power is expensive, the high water is released and discharged into the lower reservoir where power is generated.
Apart from this, HEPP can also be categorized by scale. These plants, which are divided into large-scale, small-scale, mini-scale and macro-scale, indicate the capacity to generate electricity.

-
Tidal HEPP
Tidal HEPP, also known as ebb and tide hydroelectric power plants, is installed in locations with strong tides. The energy released during strong tides is converted into electricity by the HEPP.
In this type of hydroelectric power plant, rising water is directed into a bay by means of lids. When the water rises, the turbine runs and energy is generated.

-
Depression HEPP
In deserts that lie below sea level or in hot places with sea coasts, electricity is generated by using evaporated water. Hydroelectric power plants in which this method is used are called depression power plants.
Hydroelectric power plants are also distinguished by their size:
-
Large-scale HEPP
The output of large-scale HEPPs exceeds 50 MWh. This output can meet the energy needs of 500,000 light bulbs of 100 Wh each. In other words, if the electricity demand of a house is 5 kWh, a large HEPP can generate the electricity demand of 10,000 houses. If it is assumed that 5 people live in each house, the electricity needs of 50,000 people can be met.
-
Small-scale HEPP
Small-scale HEPPs generate energy in the range of 10-50 MW. The energy generated by these HEPPs can be distributed by connecting to the national grid or used to meet the electricity needs of a residential area or a large factory.
Assuming a capacity of 10 MWh, this power can meet the energy needs of 2,000 homes.
-
Mini-scale HEPP
The output of mini-scale HEPPs ranges from 101 kWh to 10,000 kWh. With 1000 kWh, the power needs of a total of 20 houses can be met. Unlike small-scale systems, these systems contribute little to the national energy grid. They are mostly used to meet the energy needs of small settlements or fish farms on riverbanks.
-
Micro-scale HEPP
Micro-scale HEPPs are extremely small and do not provide electrical energy to the national energy grid. They are preferred in locations that are far from larger settlements and are not connected to the national energy grid. The power output of micro-scale HEPPs ranges from 200 Wh to 100 kWh. In other words, it can be used for the needs of a settlement or a farm such as lighting, heating and cooking.
What are the Advantages of Hydropower?
In addition to generating electricity in an environmentally friendly way, HEPPs have many other advantages. The first reason is the long lifetime of the plants.
At the same time, it is very beneficial because maintenance costs are low and there are no fuel costs. One of the economic advantages is that installation costs are paid off within a short period of 5-10 years. It also creates jobs in the region where it is located.
Since HEPPs have a high efficiency of 90%, they help reduce foreign dependence. Since water is a renewable resource, it is possible to maintain the benefits over a long period of time.
Another plus is the fact that it does not produce greenhouse gas emissions. Hydropower increases society's awareness of hydraulics and creates jobs. It revitalizes the economy and the social structure.
Hydroelectric Power Generation in Türkiye
The amount of energy generated by hydroelectric power plants in Turkey alone in 2019 was 68,452 GWh. The installed capacity of hydroelectric power plants is increasing every year.
As of 2020, there were 653 HEPPs nationwide. However, the amount of energy generated from hydropower changes every year due to climatic conditions. Nevertheless, it has a large share in energy production. In Turkey, the Aydem hydroelectric power plant continues to focus on renewable energy.
Hydroelectric Power Generation in the World
The use of hydroelectric power, which occupies an important place among renewable energy sources, is gradually increasing in the world.
In 2018, hydroelectric power generation worldwide reached an annual average of 4,200 TWh.
The country with the highest hydropower potential is China with 352 GWh. China is followed by Brazil with 104 GWh, the USA with 103 GWh and Canada with 81 GWh. These 4 countries produce about 50% of the total HEPP capacity installed worldwide.
The Largest Hydroelectric Power Plants in the World
- The Three Gorges Dam in China, built between 2008 and 2012, is the largest hydropower plant in the world with a capacity of 22,500 MWh.
- The Itaipu Dam in Brazil, inaugurated in 1984, is the second largest hydropower plant in the world with a capacity of 14,000 MWh.
- The Xiluodu Dam in China is the second largest hydropower plant in China and the third largest in the world. Built in 2014, the dam has a capacity of 13,860 MWh.
- The Belo Monte Dam in Brazil is the second largest hydropower plant in Brazil and the fourth largest in the world, with a capacity of 11,233 MWh. Its installation was completed in 2019.
- The Guri Dam in Venezuela is the fifth largest hydropower plant in the world. Completed in 1986, the dam has a capacity of 10,240 MWh.
- The Tucuruí Dam, also built in Brazil, is the sixth largest hydropower plant with a capacity of 8,370 MWh. Although it was installed in 1984, it was not officially completed until 2012.
- In 7th place is the Grand Coulee Dam in America. This hydroelectric power plant with a capacity of 6,800 MWh was opened in 1942.
- The Xiangjiaba Dam is also located in China. The capacity of this HEPP, which was officially opened in 2012, is 6,448 MWh.
- China's Longtan Dam has a capacity of 6,426 MWh. The HEPP with the 9th largest capacity was inaugurated in 2009.
- The Sayano-Shushenskaya Dam in Russia, commissioned in 1978, ranks 10th among the largest HEPPs with a capacity of 6,400 MWh.

Three Gorges Dam, World's largest hydropower plant
Image Source: Creative Commons
History of Hydropower
For as long as mankind has existed, water has been used for various purposes. About 2000 years ago, the Greeks built water wheels to extract flour from wheat. In the 3rd century BC, the Egyptians used Archimedes' water screw for irrigation.
The use of modern hydroelectric turbines began in the mid-1700s. In 1880, a dynamo driven by a water turbine was used to light a theater and a store in Michigan.
Later, in 1881, a dynamo connected to the turbine of a flour mill was used for street lighting in Niagara Falls. In the systems of that era, power was transmitted using direct current.
With the alternating current used today, energy can be transmitted over longer distances. The Redlands Power Plant, built in California in 1893, is the first AC hydroelectric power plant. This power plant, which uses water wheels, is driven by a three-phase generator that provides even power distribution.
Comparison of Hydropower and Other Energy Sources
Hydropower has a number of technical advantages compared to other renewable energy sources. The first is that it is a safe energy.
Another advantage is that the energy generated can be stored and used when needed. HEPPs with storage make this possible. In addition, it is a great advantage that HEPPs with low capacity can be converted into systems with high capacity in a few seconds.
HEPPs are a power generation method with low operating costs, long operating life, and high efficiency at the same time. Although the initial investment cost is high, it has the advantage that this cost is paid off in a short time and the maintenance and repair costs are very low.
In addition, the unit price of the energy generated is favorable. Most of the investment made for HEPP is domestic expenditure and contributes to local development. It is also an important resource that reduces dependence on foreign countries.
You can share all your opinions, comments and questions about hydropower with us in the comment box below.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment