What is in this article?
Isotopes are known as versions of atoms that belong to the same element but have different mass numbers, lifting a veil of mystery in the world of science. Today, isotopes play an important role not only in laboratories of scientists but also in a broad range of applications from medicine to industry, power generation and environmental analyses. We are now going to discover what isotopes are, how they are generated and where they are used, and take a closer look at the value these subatomic particles add to the modern world. This journey we are taking on towards the world of isotopes will reveal the secrets in the depths of science and the applications where isotopes shape our daily lives.
 What is an Isotope, the Mysterious Side of an Atom?
What is an Isotope, the Mysterious Side of an Atom?
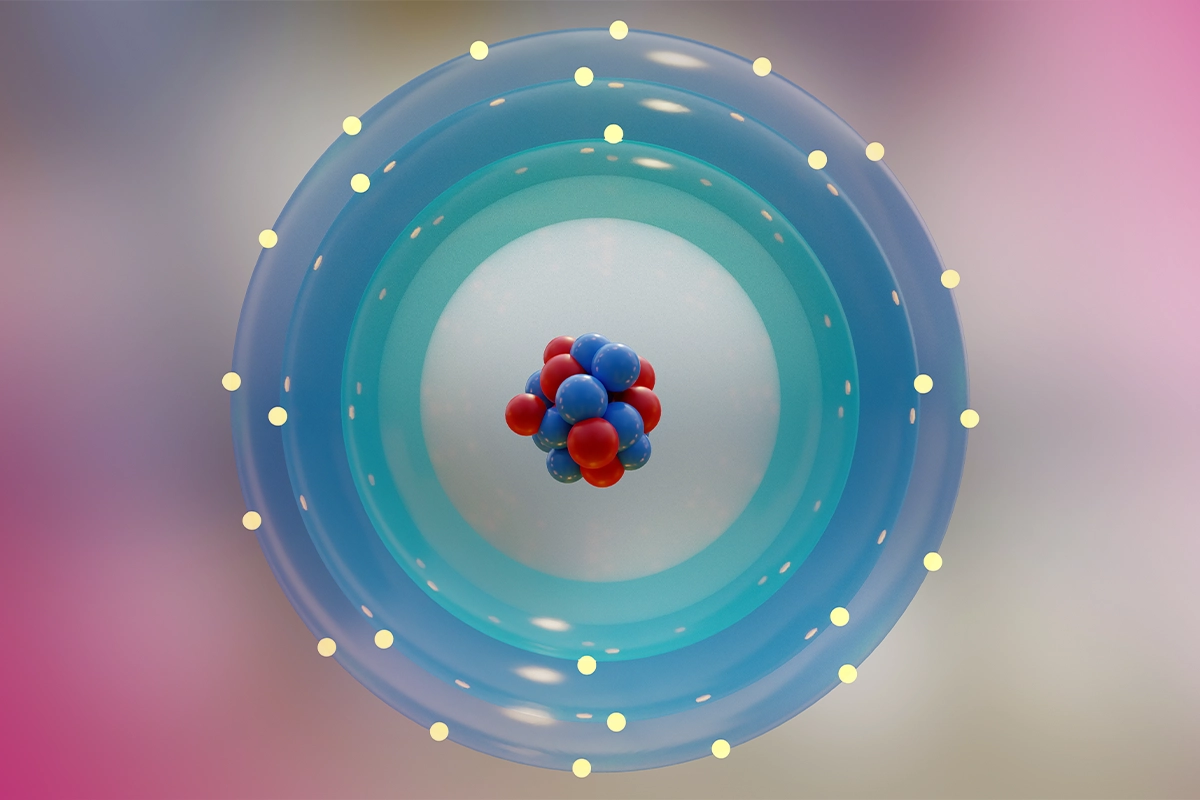
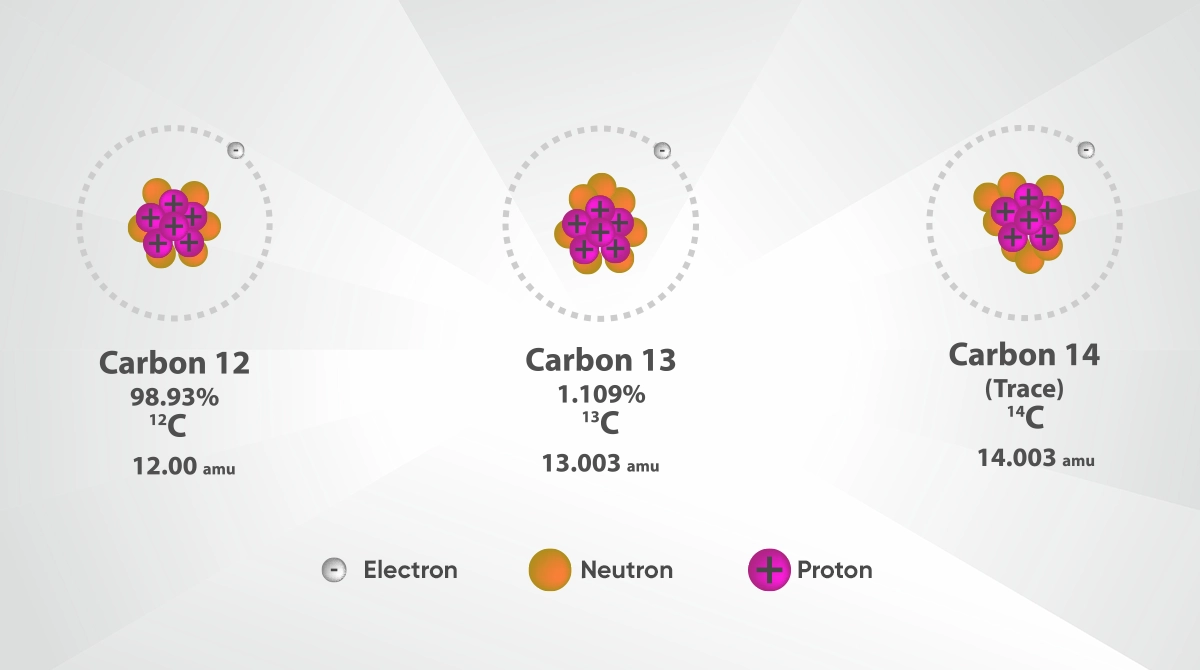
Atoms may differ in terms of mass numbers even though they belong to the same element. The reason for such difference in mass is that the number of protons remains the same while the number of neutrons changes. The type of atoms with such different mass numbers are called “isotopes”. Although isotopes generally have similarities in terms of chemical properties, their physical properties may vary considerably. For example, the element carbon has different isotopes like Carbon-12, Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 Each isotope is a version of the same element with a different mass.
Understanding the properties of isotopes is of great importance for modern science. If different isotopes have properties especially like radioactivity, they are commonly used in medicine and industry. This allows them to contribute to solving various problems both in life sciences and engineering. Radioactive isotopes can be used for cancer treatment in medicine while stable isotopes can be utilized in food analyses or environmental research. Unique characteristics of isotopes have made them an importance research topic for science.
Discover the Structure of Isotopes
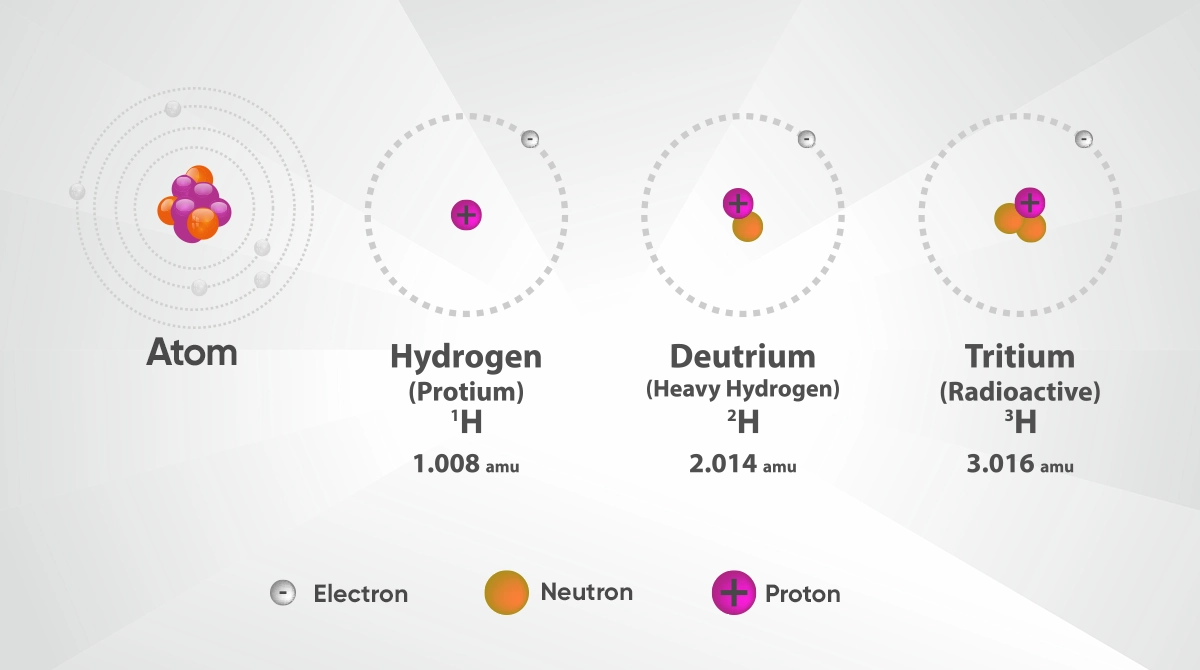
The basic structures comprising the isotope of an atom are protons, neutrons and electrons. Atomic numbers of elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. This way, atoms belonging to the same element have the same chemical properties. However, these atoms with different numbers of neutrons, i.e. isotopes, are differentiated by mass numbers. For example, the most common isotope of hydrogen contains only one proton, while its isotopes called deuterium and tritium contain one or two more neutrons. This structural difference causes certain physical properties of isotopes to be different.
The relevant difference in the number of neutrons in turn affect stability of isotopes. Stable isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay in time while unstable isotopes can turn into a different element in time. This conversion process is called “radioactive decay”. Many radioactive isotopes automatically undergo this process in nature and radiate energy. Properties of radioactive isotopes allow them to be used in both scientific research and medical applications. Because understanding such differences in the structure of isotopes is key to use them effectively in the right fields.
5 Most Common Isotopes
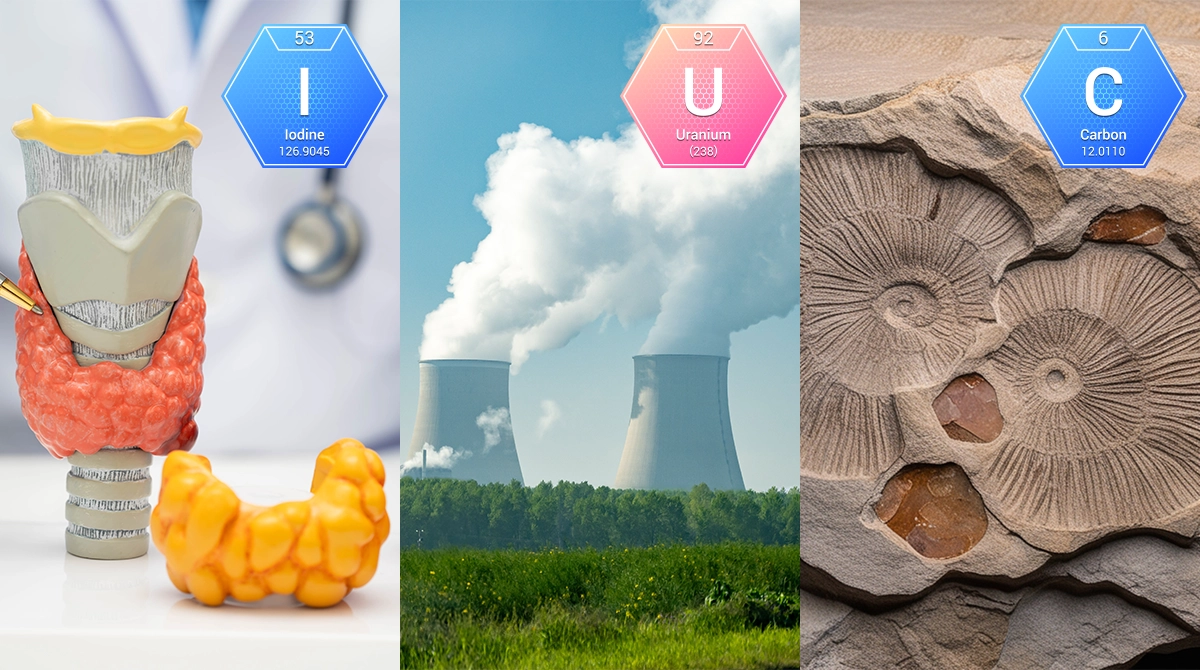
Some isotopes frequently encountered in nature and laboratory environments play quite important roles in the world of science. Some of the most common isotopes are carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14, which contain three different isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are used in chemical and biological research due to their stable structure, while carbon-14, due to its radioactive properties, plays an important role in calculating the age of archeological findings.
Another most commonly used isotope is iodine-131. As a radioactive isotope, iodine-131 is especially effective for thyroid cancer in medicine. On the other hand, uranium-235 and uranium-238 isotopes have a critical role in nuclear power generation and manufacture of nuclear weapons. Lastly, protium, deuterium and tritium, which are isotopes of hydrogen, are isotopes most commonly found in universe. Especially found in heavy water structure, deuterium contributes to power generation in nuclear reactors. Said isotopes are widely used not only in scientific research but also in energy, medicine and industry fields.
 Chemical and Physical Properties of Isotopes
Chemical and Physical Properties of Isotopes
Chemical properties of isotopes are usually similar as they belong to the same element. Having the same atomic number as a result of having the same number of protons, isotopes demonstrate similar behavior in chemical reactions. However, the difference in the number of neutrons affect their physical properties. For example, the mass difference may lead to differences in physical properties of isotopes such as density or melting point. Therefore, it may be observed that they demonstrate distinguishing properties in certain physical processes.
Chemical properties of radioactive isotopes remain the same as stable isotopes while their physical properties differentiate. Radioactive isotopes may decay in time and convert into a different element and radiate energy during such conversion. This resulting property makes radioactive isotopes important for energy production, cancer treatment and radiation-based imaging techniques. Furthermore, stable isotopes are preferred in numerous fields such as environmental pollution measurement in environmental research and industry. Isotopes that are chemically similar but have different physical properties play important roles in various applications thanks to their versatile characteristics.
10 Areas of Use for Isotopes
Known for their versatile properties, isotopes are used in a wide range of areas from science to medicine, industry and environmental research. One of the most commonly known area of use is medicine. In particular, radioactive isotopes are used in cancer treatment, tumor diagnosis and other diagnosis methods. They are also used in sterilization procedures to help make medical devices safe to use.
Another important area of use is power generation. Isotopes like uranium-235 are used to produce energy at nuclear power plants. Radioactive isotopes that are used in agriculture, on the other hand, help monitor plant growth processes and pest control. Environmental science is also one of the fields where isotopes are used effectively. Isotopes like carbon-14 are used to get information about the history of fossil fuels and the carbon cycle in atmosphere. Archeology, geology, industrial quality control and food security, among many others, are some of the numerous fields where isotopes are important elements that make life easier.
 Future of Isotopes
Future of Isotopes
Isotopes today are already used in a very wide range of applications and they are expected to be used in many more areas in the future. Especially new research in medicine and energy show that isotopes have a critical role in developing innovative treatment methods and sustainable energy solutions. Use of targeted radioactive isotopes is going to become more common in advanced diagnosis and treatment techniques. This will allow to treat diseases more effectively.
It is also anticipated that isotopes will be used more broadly in environmental and climate change research in the future. Carbon isotopes will become even more important to study the effects of climate change in the previous periods and analyze human impact on the environment. Studies aimed at improving the sustainability of nuclear power sources will also allow isotopes to be used more efficiently in the energy sector. All of these advances show that isotopes are a critical scientific instrument not for today’s world but also for the future.
It is crystal clear that isotopes have a great potential both in today’s world and for the future. From medicine to energy, environmental science and agriculture, isotopes offer innovative solutions in numerous fields to keep making life easier for us. So, what do you think will be the most exciting area of use for isotopes in the future? What do you think about the developments in this field?

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment