
What is in this article?
A ceraunophile is someone who loves lightnings, thunderbolts and thunders. Some people love the weather when there is continuous thunder and lightning, while for some it is a complete nightmare.
Every second, 100 lightnings and thunderbolts on average occur in different regions on Earth. Heating the surrounding air up to 5 times the surface of the Sun, which corresponds to almost 30,000°C, this electrically charged natural phenomenon threatens numerous living and non-living things, humans in particular.
The lightning that is formed due to the differences in electrical charge between clouds is called a thunderbolt when there is an energy transfer between negatively charged clouds and the earth. Thunderbolts have around 10 times more electrical energy than that on high voltage lines. Thunderbolts may have fatal consequences as they cause forest fires and numerous material damages, and harm human beings and animals. Although thunderbolts leave a human’s body in just three milliseconds, they might lead to permanent damages or even death. That is why it is quite important to understand the nature of thunderbolts and take measures against them in stormy weathers. Let’s take a closer look at how lightnings, thunderbolts and accompanying thunders are formed.
What is a Lightning
Lightnings are weather events that occur either between clouds or between clouds and the earth. In the simplest terms, they are electrical sparks formed when there is a balance disorder between the positive and negative charges in air.
Lightnings can be divided into three main categories. This categorization is based on where a lightning starts and where it ends. A lightning can occur either within a cloud, between two clouds or between clouds and the earth. Lightnings between clouds and the earth are also called thunderbolts.
The thing that illuminates the sky and creates magnificent views in stormy weathers is the static electricity. You must have experienced the static electricity many times, which occurs when you rub two objects against each other. The occurrence of lightnings within clouds is also related to the static electricity charge.
In order to better understand lightnings, we should brush up on what we know about clouds, from which lightnings come. Clouds are clumps where the moisture in air is condensed. Clouds contain different forms of water such as water droplets, water vapor and ice crystals, as well as other materials such as dust and sand. Because of the air currents within clouds, water droplets rise and turn to ice, while ice particles descend and melt down. Alright, but what does it have to do with lightnings?
When there is a storm, the ice crystals within clouds collide when moving at a high speed. This friction of ice crystals lead to an exchange of electrons between particles. This way, positively and negatively charged layers form within the cloud, which leads to an environment suitable for lightnings to occur.

What Causes a Lightning?
Scientists have not yet reached a definitive opinion on why lightnings occur. However, we do know exactly what causes a lightning. Lightnings occur due to a series of events within a cloud. Negative and positive charges moving within the cloud are separated from each other. The top layer of the cloud becomes positive while the bottom layer contains negative charges. The distribution of these charges within the cloud can be preserved to a certain point. When the power of the electrical fields formed exceeds the insulation threshold of the atmosphere, a lightning occurs.
What is a Thunder?
Some people find peace in stormy weathers and lightnings while for some others, it is quite scary. What makes a lightning to frightening is the thunder that is heard a few seconds after the lightning itself. High-decibel thunders sound just like an explosion and can last just a few seconds or a half minute.
We now know that thunders are heard a few seconds after lightnings as light is faster. Okay, but what causes thunders?
What Causes Thunder?
The main reason why thunders occur is that the air is instantly heated at a high speed and cools back down swiftly. Lightnings heat the air extremely as they occur. The temperature at the time of occurrence of a lightning is close to 30,000°C. To better understand how hot it is, we can say that this number is five times the temperature of the Sun’s surface.
When a lightning occurs, the surrounding air expands at a really high speed. This happens so fast that it compresses the air in front of it and leads to a shock wave, which resembles a sonic boom. This phenomenon is also called an “explosive expansion”. This sudden rise of heat and the rapid expansion in air create sounds that we call thunder.
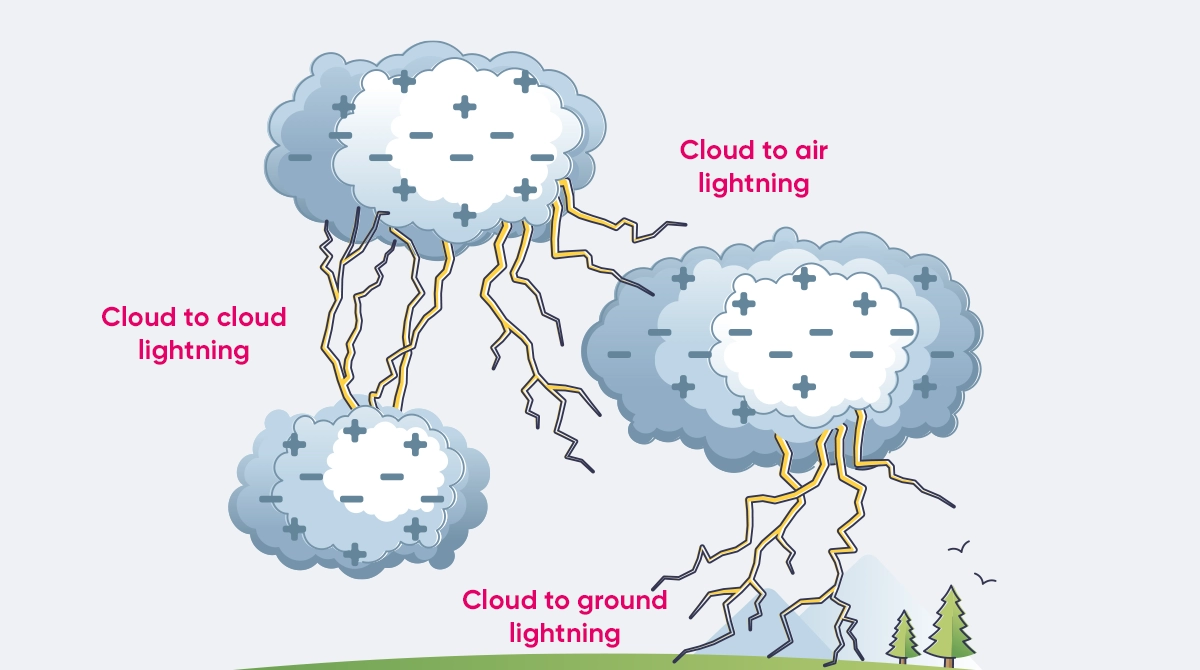
Differences Between a Lightning and a Thunderbolt
Thunderbolts are a kind of lightning. The only reason is that the electrical spark formed is between the cloud and the earth. The bottom layer of the electrically charged clouds (the layer that is closed to the earth) becomes negatively charged. Based on the principle that opposite charges attract each other, the negative charges in the cloud attract the positive charges of the earth. The negative charges in the cloud descend while the positive ones rise up. Although the atmosphere functions as insulation to prevent this gathering from happening, when a certain charge value is exceeded, an electrical discharge happens and a lightning, or a thunderbolt, occurs between the cloud and the earth.
Dangers of and Measures Against Lightnings and Thunderbolts
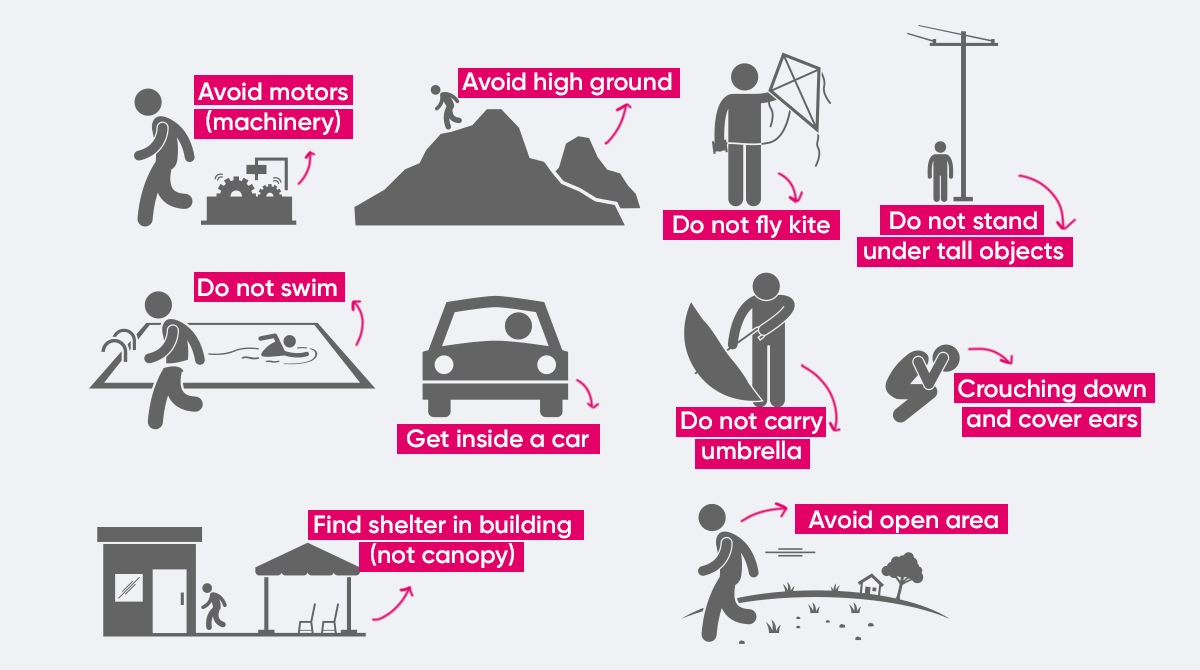
Lightnings are impressive but they are an equally dangerous natural phenomenon. Especially the combination of lightnings and thunders between the sky and the earth leads to serious threats to human life. Let us take a look at what you need to do to protect yourself against thunderbolts and stay safe in stormy weathers:
· The most effective method for protection against thunderbolts is to stay as far away as possible from the center of the storm.
· If you are in an open space and close to the storm, stay away from long metal objects (such as lamp poles), trees and other metal structures. In particular, taking shelter under a tree to avoid rain might make you the direct target of a thunderbolt.
· If you are in an open space during a storm, please go to a closed and safe area as soon as possible.
· If there are no closed spaces for shelter, you can also consider staying in your car. However, you must make sure that you do not touch the metal parts.
· Being in a closed space does not necessarily mean you are totally safe. In such places, you must stay away from glass, showers and bathtubs, radios, computers, and in particular, electronic devices with cables.
· It is important to use lightning rods in houses and at workplaces. If possible, you may consider taking shelter in buildings with a lightning rod during a storm.
· Once the lightning storm has stopped, you must wait for at least 30 minutes to go back to an open space.
Alright, pick your side: Are you one of those people who admire thunders and lightnings, or those who get concerned due to potential dangers? Tell us your opinion in the comments.


 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership






Leave a Comment