
Transformation of Garbage: How to Get Energy from Waste?
What is in this article?
Did you know that worldwide waste generation is expected to reach 4 billion 200 million metric tons by 2050? These astronomical figures are considered a result of the increasing amount and diversity of waste, inadequate waste disposal technologies and waste regulations.
Nevertheless, since it has become mandatory to ensure the efficient management of waste all over the world, landfills and efforts to generate energy from solid waste are increasing day by day.
How is all this waste and garbage that we leave to the world transformed into energy? What percentage of the energy produced in Turkey is obtained from solid waste?
You can find the answers to these and many other questions in detail in our article.
How to Generate Energy from Waste?
There are various methods to produce energy from waste. The path to be followed for this purpose is selected according to the raw material to be used and the desired product.
Wet fermentation, dry fermentation, pyrolysis, incineration, landfill methods and gasification can be used to obtain energy from waste. The raw materials required for wet and dry fermentation are also called biomass resources.
|
BONUS: According to the Biomass Energy Potential Atlas (BEPA) prepared by the Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources, the economic energy value of waste that can be used for energy production in Turkey is about 3.9 MTEP per year. |
Techniques for Electricity Generation from Waste
Wet fermentation, one of the most commonly used methods, is suitable for organic waste with low dry matter content. In this method, organic wastes such as cow, layer and slaughterhouse wastes, rotten vegetables and fruits, or food wastes are first enriched with water.
These raw materials are then fermented over a period of time using a controlled fermentation system, producing methane gas. This gas is converted into electricity or thermal energy in a cogeneration plant.
Dry fermentation, another method, is ideal for organic waste with a high percentage of solid waste. This method uses animal manure and municipal waste such as food and kitchen waste.
After the separation process, these wastes are kept in sealed tanks for a period of time and methane gas is extracted from them. This gas is purified and converted into heat or electricity via cogeneration.
In processes other than wet and dry fermentation, solid wastes other than biomass sources are used. Solid wastes are divided into harmful and harmless wastes. In addition, when analyzed by source, they are divided into domestic, industrial, commercial, institutional, municipal, and residential.
Incineration uses wastes that are mostly solids and generally have no possibility of being converted into a more useful product. Municipal waste, for example, is ideal for this process. The heat released from the incinerated waste is used to produce steam, which is used to generate electricity via a turbine.
The pyrolysis method uses recyclable organic waste with a high solid content. This is usually waste with a high cellulose content such as cotton, paper and used tires. These wastes are decomposed at extremely high temperatures, releasing a large amount of pyrolytic oil with syngas, a hydrogen-dominated gas. The pyrolytic oil is then burned in the engine to generate electrical energy.
The process known as gasification primarily uses fossil waste. Various gases are produced with the help of oxygen, which is supplied in a controlled manner at a high temperature. This gas is syngas, which has a high calorific value. Syngas, also called synthesis gas, can be used directly or converted into electrical energy through processing.
The last method, landfilling, is the use of methane gas released during the storage of municipal waste. The gas is collected and extracted through appropriately laid pipes in the waste collection areas. It is then converted into electricity through combustion. This method, also known as landfilling, was used to process 77.8 metric tons of waste in Turkey in 2020.
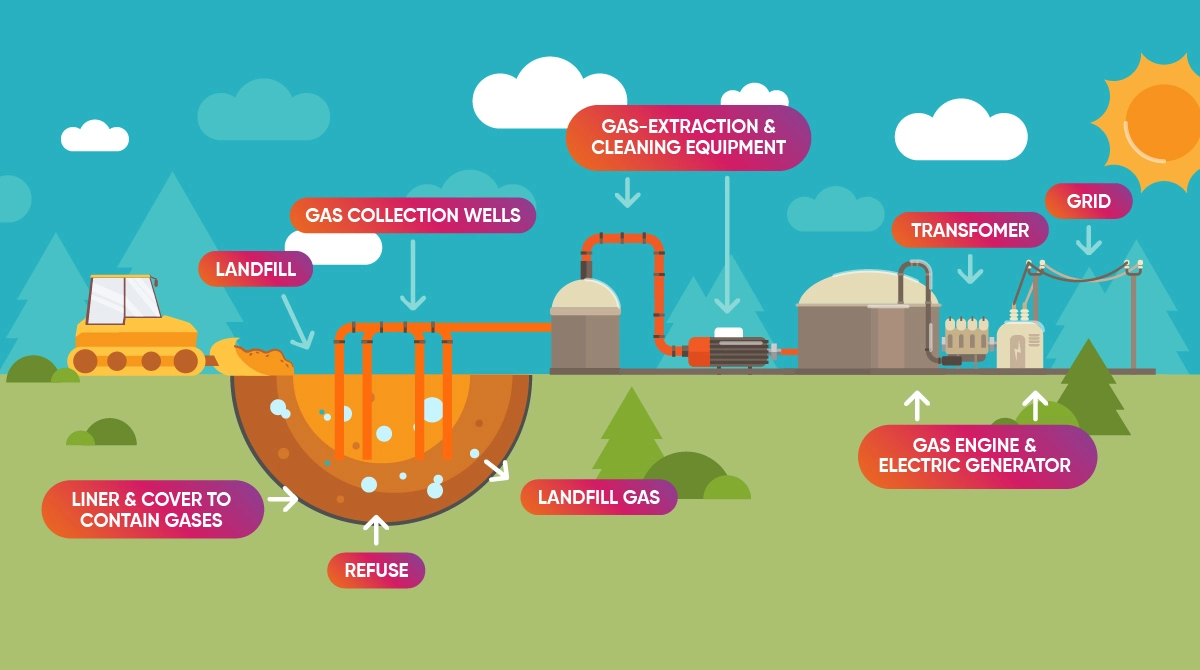
Which Wastes can be Used for Energy Generation?
Although energy generation from waste is a very common application, the range of raw materials that can be used for this method is quite wide. From forestry, animal and agricultural wastes to household wastes, from municipal wastes to industrial wastes from food factories and meat and milk processing plants, many different wastes can be used for energy production.
From this point of view, the biomass sector contributes to recycling. By selecting the right renewable energy systems for each waste, valuable products can be obtained. As a result, the carbon footprint can be reduced by realizing an environmentally friendly energy generation process.
.webp)
How can Energy be Generated from Garbage?
To understand how to generate energy from garbage, you need to know the difference between garbage and waste. After separating materials such as paper, cardboard, glass, metal and plastic that can be recycled, the remaining part that cannot be recycled is called garbage.
For this reason, waste must be stored or disposed of in an orderly manner. On the other hand, unlike garbage, waste can be reused and recycled. However, thanks to some methods, it is possible to obtain energy from garbage.
Dry fermentation, incineration, and landfilling are most commonly used to generate energy from garbage. Dry fermentation is generally preferred for the post-separation degassing of garbage from small settlements to be transported to large garbage centers. For this purpose, mechanical separation is performed after fermentation.
This separates the solids that are to be composted from those that are useless. The solid fraction is first pressed before undergoing a waste-to-fuel diversion process called Refused Drived Fuel (RDF). It is then sent to incinerators or cement plants.

Difficulties in Energy Generation from Waste
Although energy generation from waste or biomass is considered a renewable energy like solar power, it is not really a renewable type of energy. This is because combustion wastes a large amount of recyclable materials (e.g., compostable organic waste or recyclable waste such as paper) for a small amount of energy.
When these resources are recycled or composted, up to 5 times the energy produced by incineration can be saved. In addition, incineration of waste also produces carbon dioxide emissions.
Waste Energy Production and Rates in Turkey
According to Turkish Statistical Institute data for 2020, 1.3 million metric tons of waste was incinerated and energy was generated in co-incineration plants (plants that use waste as additional fuel) with waste utilization licenses.
In addition, the Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources announced that the installed capacity based on biomass and waste heat energy at the end of June 2022 was 2,172 MW. This shows that the plants providing energy from waste have a share of 2.14%, considering the total installed power in the country.
What do you think about energy generation from waste? You can share your comments with us on this topic.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership







Leave a Comment
Comments (1)
I
Igor Cambur
I want to know more about making energy from garbage